Unity Damping System
자연스러운 물리 효과를 위한 Unity용 댐핑 시스템
2025.08.04
- GitHub : Damping System
- Release : Github Release Page
DampingSystem
Unity용 2차 시스템 기반 감쇠 애니메이션 라이브러리
Youtube 영상 Giving Personality to Procedural Animations using Math을 보고 영감을 받아 만든 Unity package입니다.
There is a English translation at the bottom.
🎯 프로젝트 소개
DampingSystem은 Unity에서 자연스럽고 부드러운 애니메이션을 구현하기 위한 2차 시스템 기반 감쇠 라이브러리입니다. 물리적으로 정확한 수학 모델을 사용하여 스프링-댐퍼 시스템의 움직임을 시뮬레이션합니다.
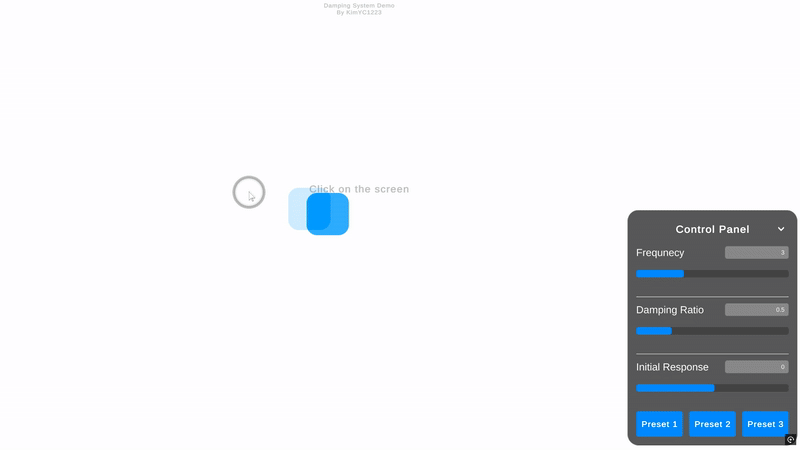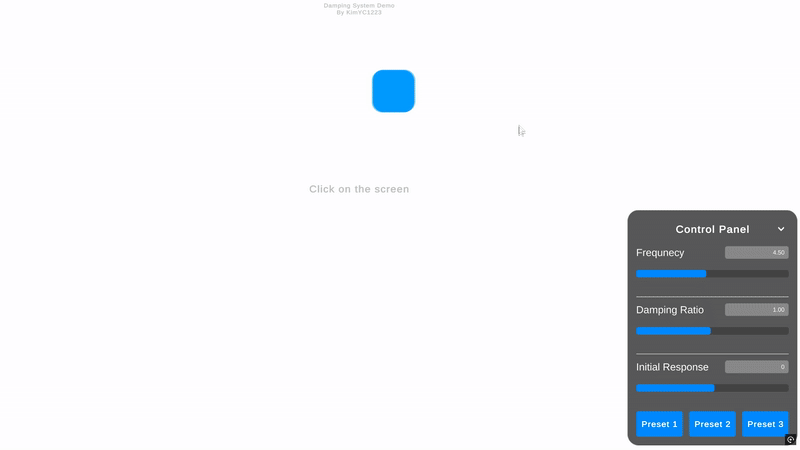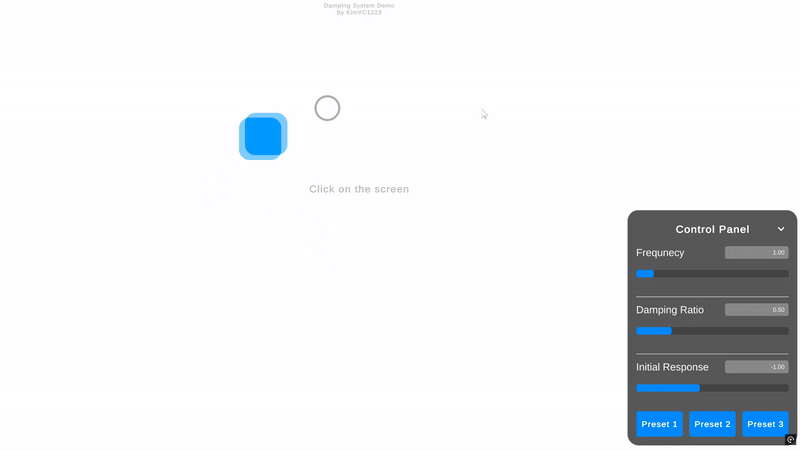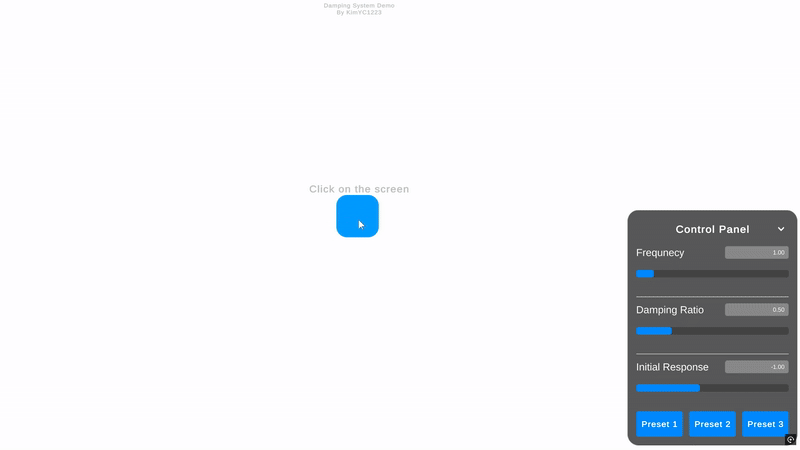
🎥 WebGL데모
프로젝트의 이해를 돕기 위한 WebGL 데모가 준비되어 있습니다!
✨ 주요 특징
- 🔬 수학적 정확성: 2차 미분방정식 기반의 물리적으로 정확한 구현
- 🎯 다양한 타입 지원: float, float2/3, Vector2/3/4 완벽 지원
- 🔧 사용 편의성: 직관적인 매개변수로 쉬운 설정
- 📚 완전한 문서화: 한국어/영어 이중 문서화
🔧 설치 방법
최신의 release된 Unity Package를 다운로드 하거나, 이 repo를 다운받으면 됩니다.
요구사항
- Unity: 2022.3.20f1 이상
🚀 빠른 시작
기본 사용법
using DampingSystem;
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
private DampingSystemVector3 positionDamper;
void Start()
{
// 감쇠 시스템 초기화
positionDamper = new DampingSystemVector3(
frequency: 2.0f, // 자연 진동수
dampingRatio: 1.0f, // 감쇠비 (1.0 = 임계감쇠)
initialResponse: 0.0f, // 초기 응답
initialCondition: transform.position
);
}
void Update()
{
// 목표 위치로 부드럽게 이동
Vector3 targetPosition = GetTargetPosition();
Vector3 smoothPosition = positionDamper.Calculate(targetPosition);
transform.position = smoothPosition;
}
}
📖 상세 사용법
매개변수 설명
| 매개변수 | 설명 | 권장값 |
|---|---|---|
frequency |
자연 진동수 (Hz) 값이 클수록 빠른 반응 |
1.0 ~ 5.0 |
dampingRatio |
감쇠비 1.0 = 임계감쇠, >1.0 = 과감쇠, <1.0 = 부족감쇠 |
0.7 ~ 1.2 |
initialResponse |
초기 응답 anticipation 효과 조절 |
0.0 ~ 0.5 |
initialCondition |
초기 조건 시작 상태값 |
현재값 |
감쇠비에 따른 동작 특성
// 부족감쇠 (Underdamped) - 진동하며 수렴
var bouncyDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// 임계감쇠 (Critically Damped) - 가장 빠른 수렴
var criticalDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// 과감쇠 (Overdamped) - 느린 수렴, 오버슈트 없음
var slowDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
커스텀 시간 간격 사용
void FixedUpdate()
{
// 고정 시간 간격 사용
float customDeltaTime = Time.fixedDeltaTime;
Vector3 result = damper.Calculate(target, customDeltaTime);
}
🧮 수학적 원리
2차 시스템 미분방정식
DampingSystem은 다음 2차 미분방정식을 기반으로 합니다:
ÿ + 2ζωẏ + ω²y = ω²x + 2ζωrẋ
여기서:
ω= 자연 각주파수 (ω = 2πf)ζ= 감쇠비r= 초기 응답 계수x= 입력 신호y= 출력 신호
자세한 내용은 이 영상을 참고하세요!
🎮 지원 타입
DampingSystem 패키지는 각각의 특정 사용 사례에 최적화된 다양한 데이터 타입별 특화 구현을 제공합니다:
스칼라 타입
// Float 감쇠 - UI 애니메이션, 체력바 등에 완벽
var floatDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float smoothValue = floatDamper.Calculate(targetValue);
Unity.Mathematics 타입
// Float2 감쇠 - Unity.Mathematics를 사용한 최적화된 2D 좌표
var float2Damper = new DampingSystemFloat2(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, new float2(0, 0));
float2 smoothPos2D = float2Damper.Calculate(targetPos2D);
// Float3 감쇠 - Unity.Mathematics를 사용한 최적화된 3D 좌표
var float3Damper = new DampingSystemFloat3(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, new float3(0, 0, 0));
float3 smoothPos3D = float3Damper.Calculate(targetPos3D);
벡터 타입
// 2D 위치 감쇠 - 2D 게임과 UI 요소에 이상적
var vec2Damper = new DampingSystemVector2(1.5f, 0.8f, 0.0f, Vector2.zero);
// 3D 위치 감쇠 - 부드러운 캐릭터/카메라 움직임용
var vec3Damper = new DampingSystemVector3(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.1f, Vector3.zero);
// 4D 벡터 감쇠 - 색상 전환, RGBA 값에 유용
var vec4Damper = new DampingSystemVector4(3.0f, 1.2f, 0.0f, Vector4.one);
구현 구조
모든 감쇠 시스템은 다음 위치의 추상 기본 클래스 DampingSystem<T>를 상속받습니다:
Assets/DampingSystem/Scripts/Abstract/DampingSystem.cs
각 타입별 구현은 다음에서 찾을 수 있습니다:
DampingSystemFloat.csDampingSystemFloat2.cs(Unity.Mathematics)DampingSystemFloat3.cs(Unity.Mathematics)DampingSystemVector2.csDampingSystemVector3.csDampingSystemVector4.cs
📊 성능 특성
벤치마크 결과
| 타입 | 연산 시간 (ns) | 메모리 사용량 |
|---|---|---|
| Float | ~15 | 64 bytes |
| Float2 | ~25 | 72 bytes |
| Float3 | ~35 | 88 bytes |
| Vector2 | ~30 | 80 bytes |
| Vector3 | ~45 | 96 bytes |
| Vector4 | ~60 | 112 bytes |
🎯 다른 라이브러리와 비교
🔷 DOTween
DampingSystem은 2차 미분방정식을 기반으로 물리 시뮬레이션을 돌려서, 자연스럽게 감쇠되는 애니메이션을 만들어주는 Unity 라이브러리입니다. frequency나 dampingRatio 같은 물리 파라미터로 움직임을 조절하고, struct 기반이라 메모리 할당 없이 15~60ns 정도의 빠른 성능을 보여줍니다.
반면 DOTween은 보간(Interpolation) 방식의 트위닝 라이브러리로, duration과 이징 함수를 이용해 애니메이션 시간을 정확히 맞추고 다양한 연출 효과를 만들 수 있습니다.
둘의 핵심 차이는 접근 방식에 있습니다. DampingSystem은 물리적으로 정확한 스프링-댐퍼 모델을 시뮬레이션하기 때문에, 목표값이 실시간으로 바뀌어도 자연스럽게 따라가는 데 강점이 있습니다. 그래서 카메라 추적이나 캐릭터 이동 같은 상황에 특히 잘 어울립니다. 반대로 DOTween은 미리 정해둔 경로나 시간을 그대로 따라가서, UI 애니메이션이나 컷신처럼 정확한 타이밍이 중요한 연출에 적합합니다.
성능만 보면 DampingSystem이 약 2~4배 빠르고 메모리 효율도 좋지만, DOTween은 더 많은 기능과 시퀀스 시스템을 갖추고 있어 다양한 연출 작업에 유리합니다.
📊 핵심 차이점
| 항목 | DampingSystem | DOTween |
|---|---|---|
| 수학적 기반 | 2차 미분방정식 기반 물리 시뮬레이션 | 보간 기반 애니메이션 |
| 의존성 | Unity 내장 기능만 사용 | 외부 라이브러리 |
| 메모리 할당 | 제로 할당 (struct 기반) | 객체 풀링 필요 |
| 성능 | 15-60ns (타입별) | 100-200ns |
| 애니메이션 스타일 | 물리적으로 자연스러운 움직임 | 다양한 이징 함수 |
| 제어 방식 | 물리 매개변수 (frequency, damping) | 시간 기반 (duration, delay) |
DampingSystem을 선택해야 하는 경우
✅ 자연스러운 물리적 움직임이 필요한 경우
카메라 추적, 캐릭터 이동, UI 요소의 부드러운 반응
✅ 실시간 반응형 애니메이션이 필요한 경우
목표값이 계속 변하는 상황 (마우스 추적, 플레이어 따라가기)
✅ 물리적 특성을 조절하고 싶은 경우
감쇠비, 진동수 등
DOTween을 선택해야 하는 경우
✅ 정확한 시간 제어가 필요한 경우
컷신, 시퀀스 애니메이션, 타이밍이 중요한 연출
✅ 다양한 이징 효과가 필요한 경우
Ease In/Out, Bounce, Elastic 등의 특수 효과
✅ 복잡한 애니메이션 체인이 필요한 경우
순차적 애니메이션, 콜백, 이벤트 시스템
✅ UI 애니메이션에 특화된 기능이 필요한 경우
크기, 회전, 색상 변경 등의 다양한 프로퍼티 애니메이션
🔗 참고자료
English translation
DampingSystem

Second-Order Damping Animation Library for Unity
Youtube video Giving Personality to Procedural Animations using Math inspired Unity package.
상단에 한국어 번역이 있습니다.
🎯 Project Introduction
DampingSystem is a second-order system based damping library for creating natural and smooth animations in Unity. It simulates spring-damper system motion using physically accurate mathematical models.
🎥 WebGL Demo
To help you understand the project, I have prepared a WebGL demo!

✨ Key Features
- 🔬 Mathematical Accuracy: Physically accurate implementation based on second-order differential equations
- 🎯 Multiple Type Support: Full support for float, float2/3, Vector2/3/4
- 🔧 Ease of Use: Easy setup with intuitive parameters
- 📚 Complete Documentation: Fully documented in both Korean and English
🔧 Installation
Download the latest released Unity Package or download this repository.
Requirements
- Unity: 2022.3.20f1 or higher
🚀 Quick Start
Basic Usage
using DampingSystem;
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
private DampingSystemVector3 positionDamper;
void Start()
{
// Initialize damping system
positionDamper = new DampingSystemVector3(
frequency: 2.0f, // Natural frequency
dampingRatio: 1.0f, // Damping ratio (1.0 = critical damping)
initialResponse: 0.0f, // Initial response
initialCondition: transform.position
);
}
void Update()
{
// Smooth movement to target position
Vector3 targetPosition = GetTargetPosition();
Vector3 smoothPosition = positionDamper.Calculate(targetPosition);
transform.position = smoothPosition;
}
}
📖 Detailed Usage
Parameter Description
| Parameter | Description | Recommended Values |
|---|---|---|
frequency |
Natural frequency (Hz) Higher values = faster response |
1.0 ~ 5.0 |
dampingRatio |
Damping ratio 1.0 = critical, >1.0 = overdamped, <1.0 = underdamped |
0.7 ~ 1.2 |
initialResponse |
Initial response Controls anticipation effect |
0.0 ~ 0.5 |
initialCondition |
Initial condition Starting state value |
Current value |
Behavior by Damping Ratio
// Underdamped - oscillates to convergence
var bouncyDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// Critically Damped - fastest convergence
var criticalDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// Overdamped - slow convergence, no overshoot
var slowDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
Custom Time Step Usage
void FixedUpdate()
{
// Using fixed time step
float customDeltaTime = Time.fixedDeltaTime;
Vector3 result = damper.Calculate(target, customDeltaTime);
}
🧮 Mathematical Principles
Second-Order System Differential Equation
DampingSystem is based on the following second-order differential equation:
ÿ + 2ζωẏ + ω²y = ω²x + 2ζωrẋ
Where:
ω= Natural angular frequency (ω = 2πf)ζ= Damping ratior= Initial response coefficientx= Input signaly= Output signal
For detailed information, refer to this video!
🎮 Supported Types
The DampingSystem package provides specialized implementations for different data types, each optimized for their specific use cases:
Scalar Types
// Float damping - perfect for UI animations, health bars, etc.
var floatDamper = new DampingSystemFloat(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float smoothValue = floatDamper.Calculate(targetValue);
Unity.Mathematics Types
// Float2 damping - optimized for 2D coordinates using Unity.Mathematics
var float2Damper = new DampingSystemFloat2(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, new float2(0, 0));
float2 smoothPos2D = float2Damper.Calculate(targetPos2D);
// Float3 damping - optimized for 3D coordinates using Unity.Mathematics
var float3Damper = new DampingSystemFloat3(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, new float3(0, 0, 0));
float3 smoothPos3D = float3Damper.Calculate(targetPos3D);
Vector Types
// 2D position damping - ideal for 2D games and UI elements
var vec2Damper = new DampingSystemVector2(1.5f, 0.8f, 0.0f, Vector2.zero);
// 3D position damping - for smooth character/camera movement
var vec3Damper = new DampingSystemVector3(2.0f, 1.0f, 0.1f, Vector3.zero);
// 4D vector damping - useful for color transitions, RGBA values
var vec4Damper = new DampingSystemVector4(3.0f, 1.2f, 0.0f, Vector4.one);
Implementation Structure
All damping systems inherit from the abstract base class DampingSystem<T> located in:
Assets/DampingSystem/Scripts/Abstract/DampingSystem.cs
Each type-specific implementation can be found in:
DampingSystemFloat.csDampingSystemFloat2.cs(Unity.Mathematics)DampingSystemFloat3.cs(Unity.Mathematics)DampingSystemVector2.csDampingSystemVector3.csDampingSystemVector4.cs
📊 Performance Characteristics
Optimization Techniques
Benchmark Results
| Type | Operation Time (ns) | Memory Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Float | ~15 | 64 bytes |
| Float2 | ~25 | 72 bytes |
| Float3 | ~35 | 88 bytes |
| Vector2 | ~30 | 80 bytes |
| Vector3 | ~45 | 96 bytes |
| Vector4 | ~60 | 112 bytes |
🎯 Comparison with Other Libraries
🔷 DOTween
DampingSystem is a Unity library that simulates second-order differential equations to create smooth, natural damping animations. You can tweak the motion using physical parameters like frequency and dampingRatio, and since it’s built on a struct-based design, it runs with zero memory allocations and delivers lightning-fast performance—around 15–60ns per update.
DOTween, on the other hand, is an interpolation-based tweening library. It lets you control animation precisely over a set duration using easing functions, making it easy to create a wide variety of animation effects.
The key difference lies in their approach. DampingSystem uses a physically accurate spring-damper model, so it responds naturally even when the target value changes in real time. This makes it great for things like camera tracking or character movement. DOTween, in contrast, follows predefined paths and timings, making it ideal for UI animations, cutscenes, or anything where precise timing is essential.
In terms of raw performance, DampingSystem can be about 2–4× faster and more memory-efficient. But DOTween shines when it comes to rich features and its sequencing system, which gives you a lot of flexibility for complex animations.
📊 Differences
| Items | DampingSystem | DOTween |
|---|---|---|
| Mathematical Basis | Second-Order Differential Equation-Based Physics Simulation | Interpolation-Based Animation |
| Dependencies | Uses only Unity built-in functions | External Libraries |
| Memory Allocation | Zero-Allocation (struct-based) | Requires Object Pooling |
| Performance | 15-60ns (depending on type) | 100-200ns |
| Animation Style | Physically Natural Movements | Various Easing Functions |
| Control Method | Physics Parameters (frequency, damping) | Time-Based (duration, delay) |
When to Choose DampingSystem
✅ When you need natural physical movement
Camera tracking, character movement, smooth UI element response
✅ When you need real-time responsive animation
When target values constantly change (mouse tracking, player following)
✅ When you want to control physical properties
damping ratio, frequency, etc.
When to Choose DOTween
✅ When you need precise timing control
Cutscenes, sequence animations, and timing-critical productions
✅ When you need various easing effects
Special effects such as Ease In/Out, Bounce, and Elastic
✅ When you need complex animation chains
Sequential animation, callbacks, and event systems
✅ When you need specialized features for UI animation
Various property animations such as size, rotation, color change, etc.
